Electric Motor Thermal Management for EVs and PHEVs
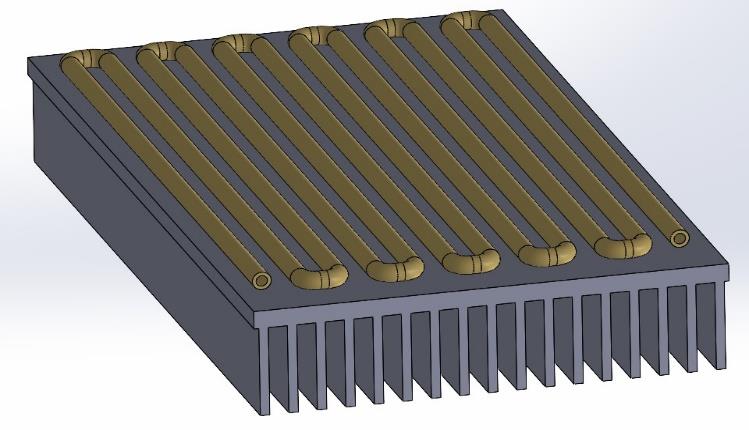
An alternative thermal management system is proposed to cool down an electric motor of an EV. The design uses a ninety percent ethylene glycol-water mixture as the coolant, and it utilizes a combined cooling system that comprises of a cylindrical housing that covers the motor and absorbs the heat, and an aluminum heat sink on the base of the car to dissipate that heat.
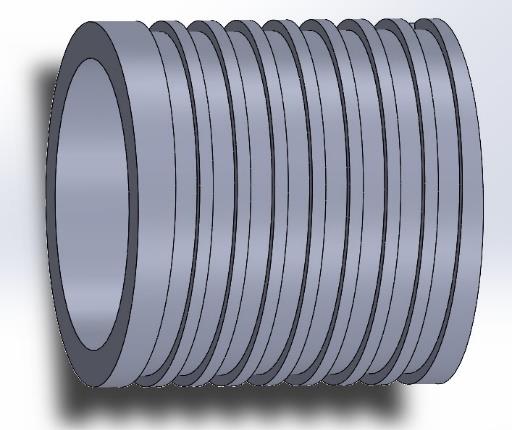

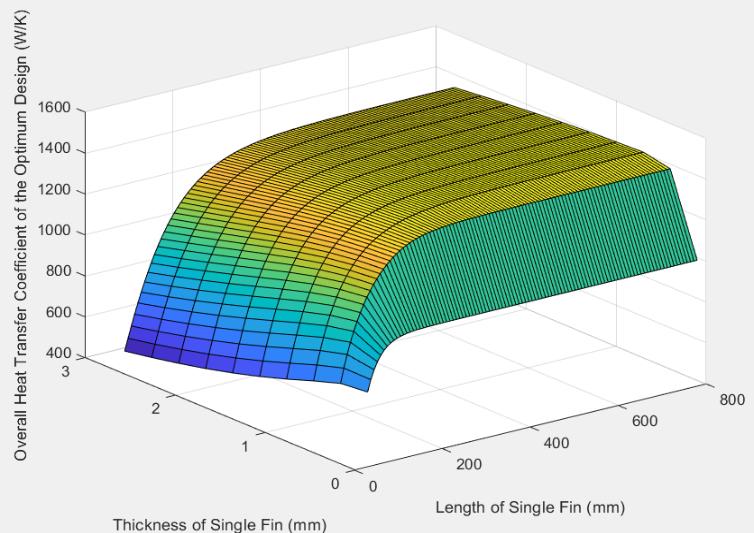
After the concept design phase, free variables are optimized in a way that maximize the heat dissipation and minimize the pressure losses. Appropriate governing and boundary equations are derived and formulated in accordance with the literature. Then, these equations are fed to an algorithm to iteratively find the optimum design parameters using MATLAB.
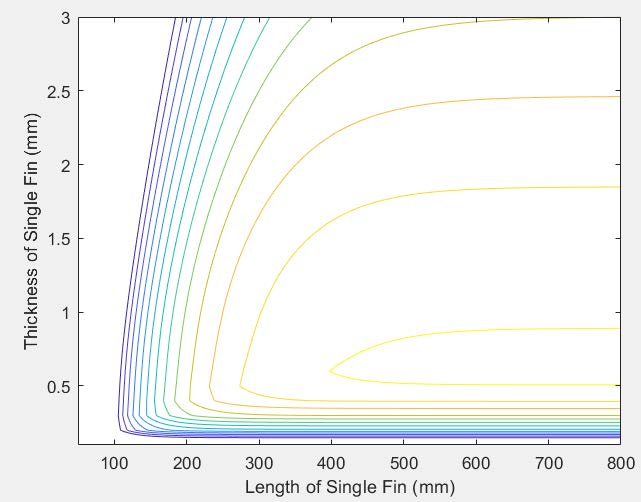
Validation of the model is done via Ansys Fluent tool, a finite element computer software. All the parameters, equations, and constraints are entered to the software along with the optimum geometry of the components. Solidworks is used to create three main components:
- Heat Tubes
- Heat Sink
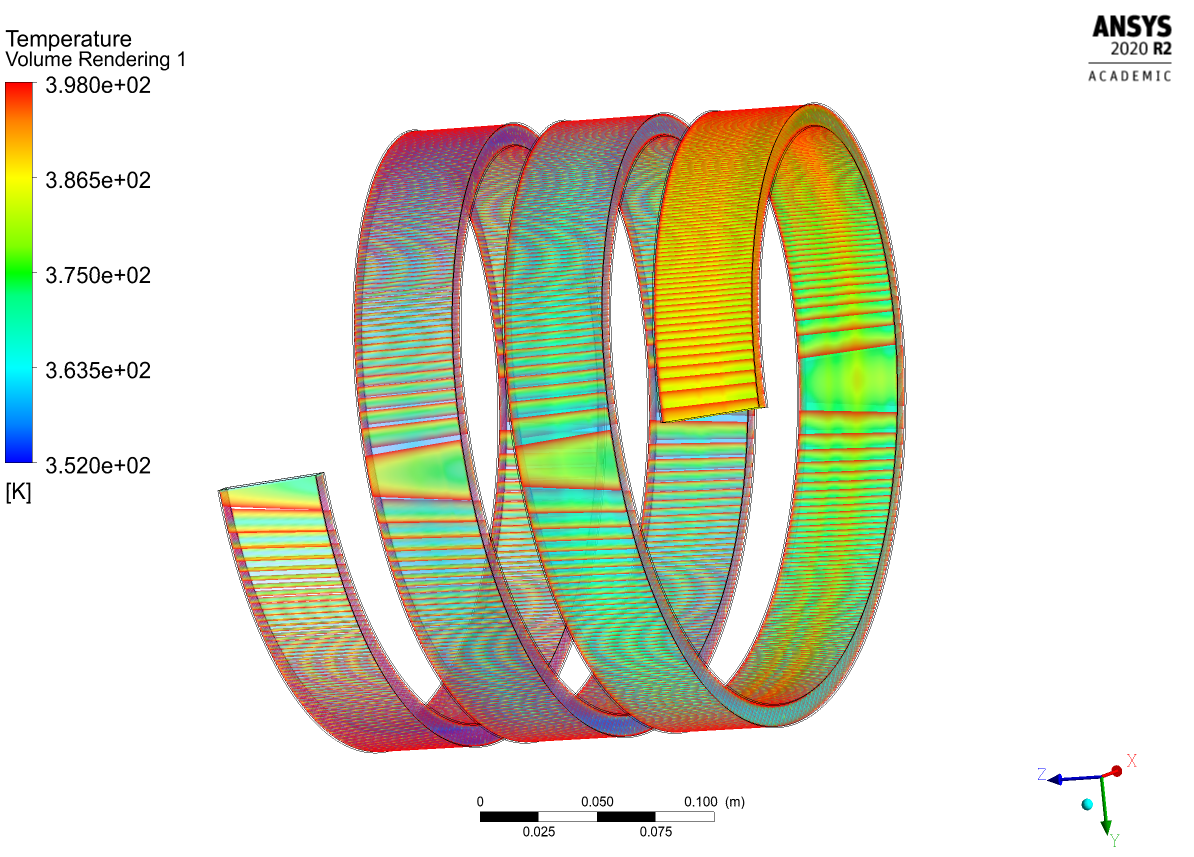
- Cooling Cylinder
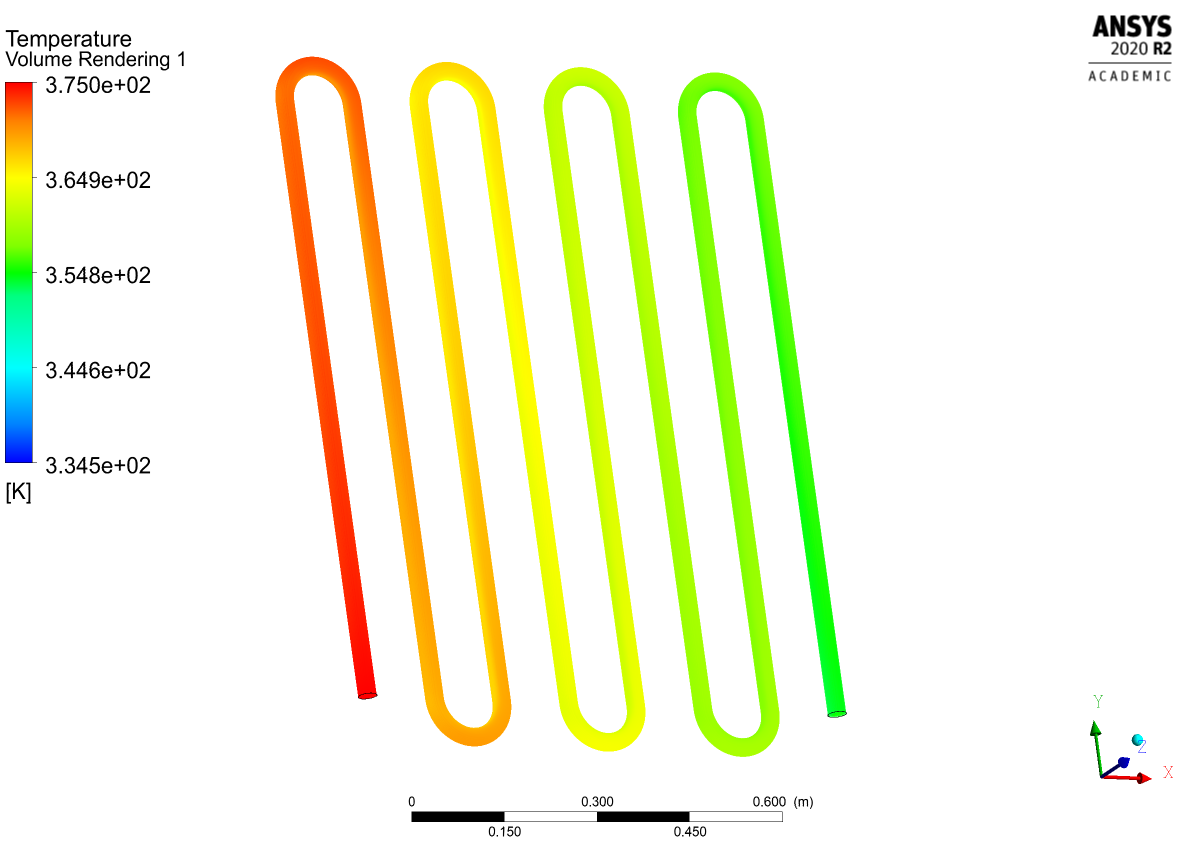
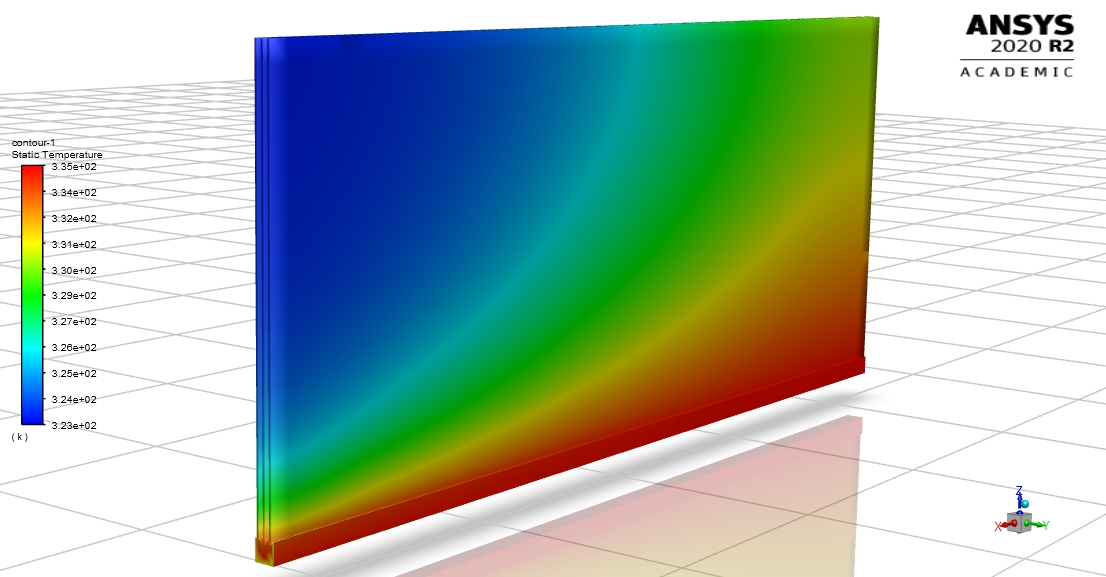
The solution is obtained by making iterations until the residuals converge to a small, predetermined limiting value.
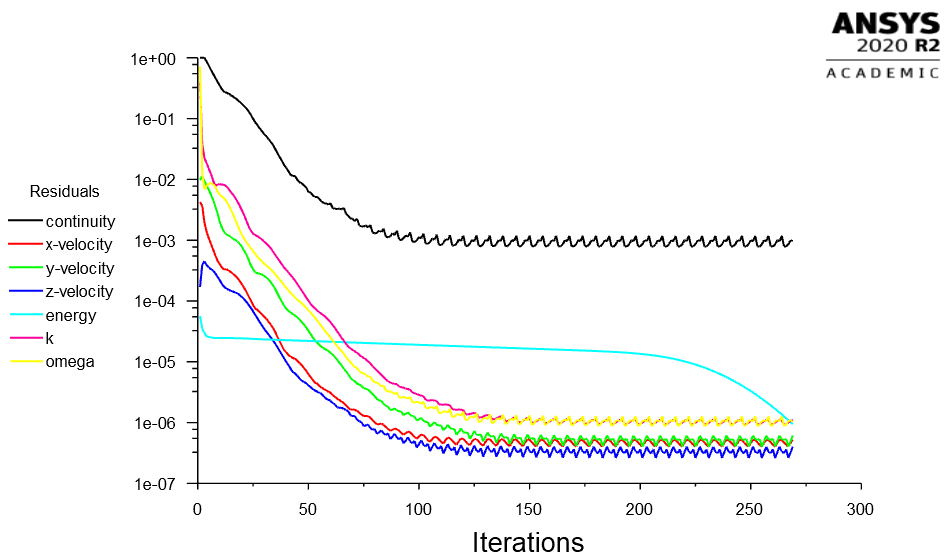
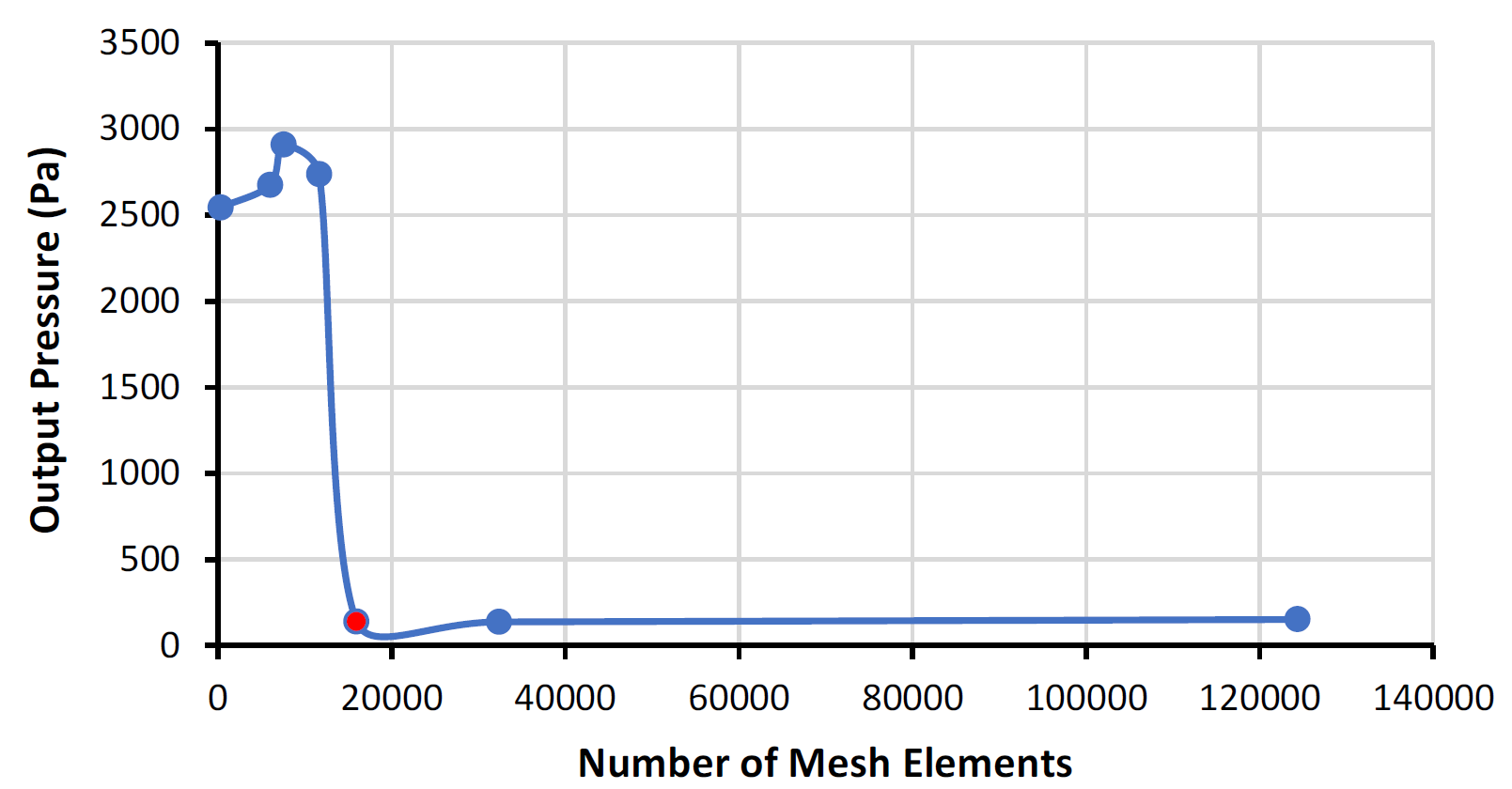
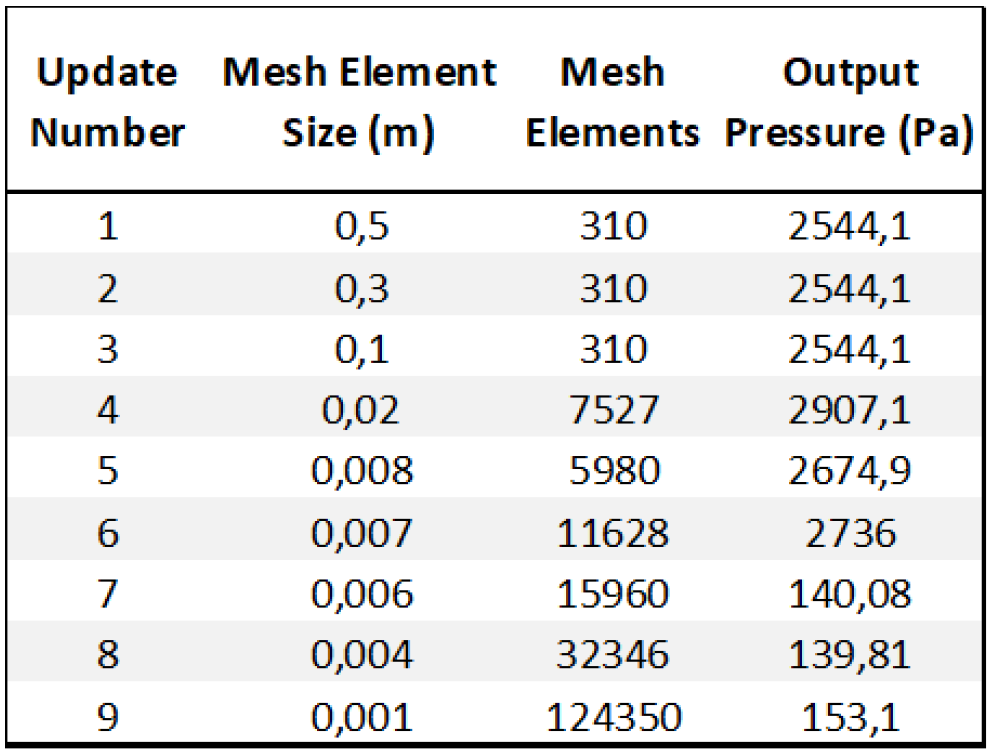
Grid independence test is carried out for each element by trying different mesh sizes and observing the differences in the output pressures. When variations in the resulting parameter are not significant after a certain mesh element size, that size is selected as an ideal mesh element size, since increasing it after that point would only increase the necessary computational work.